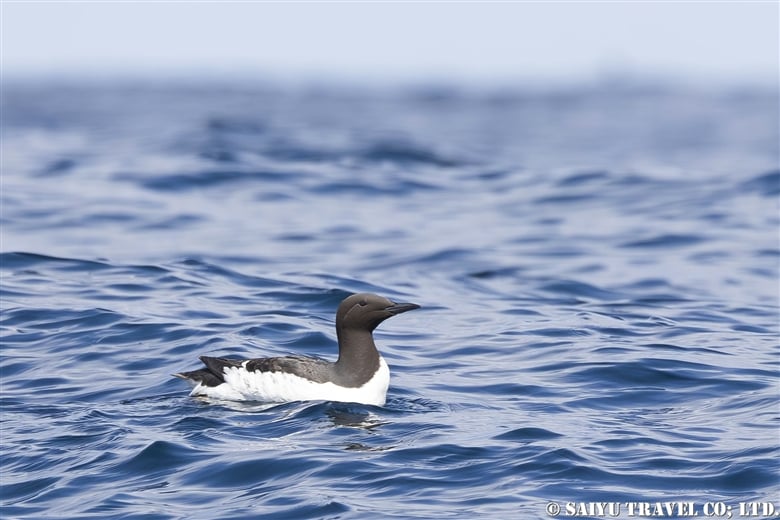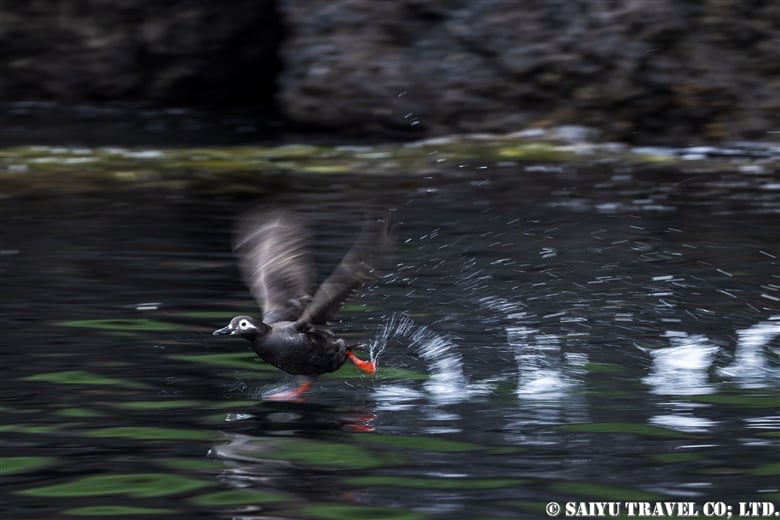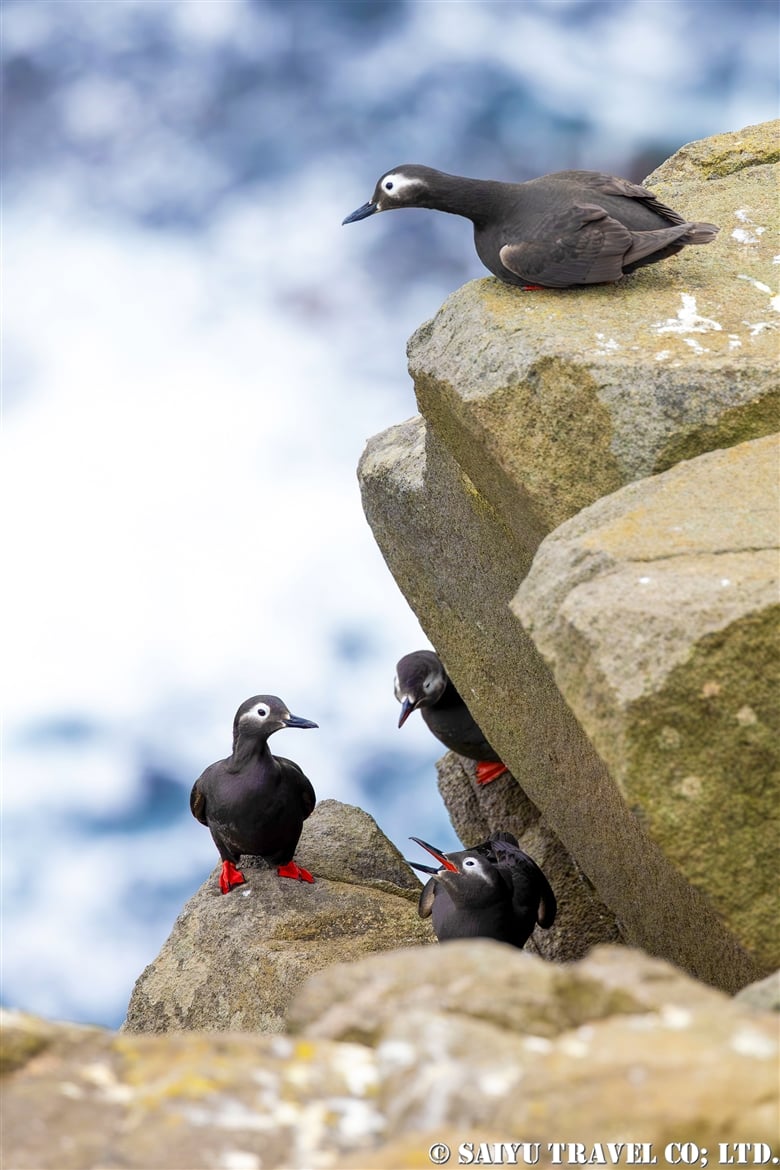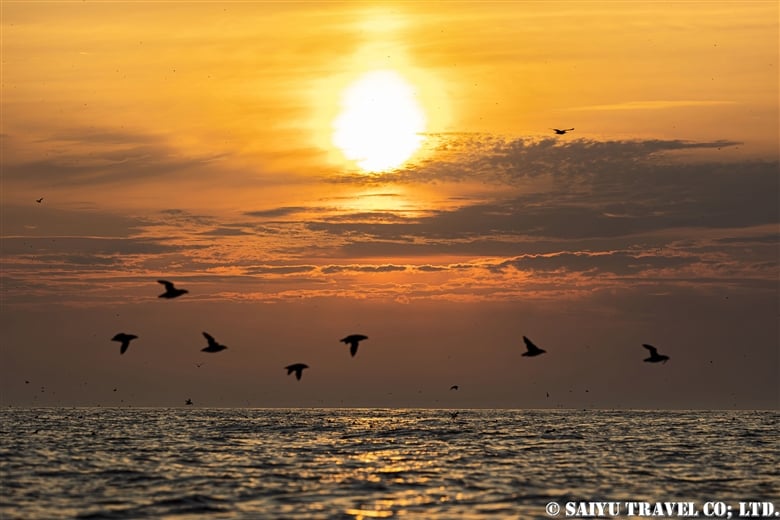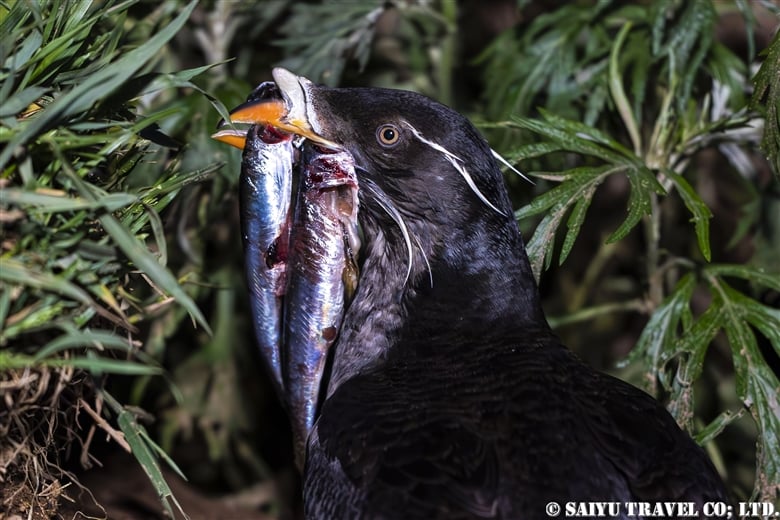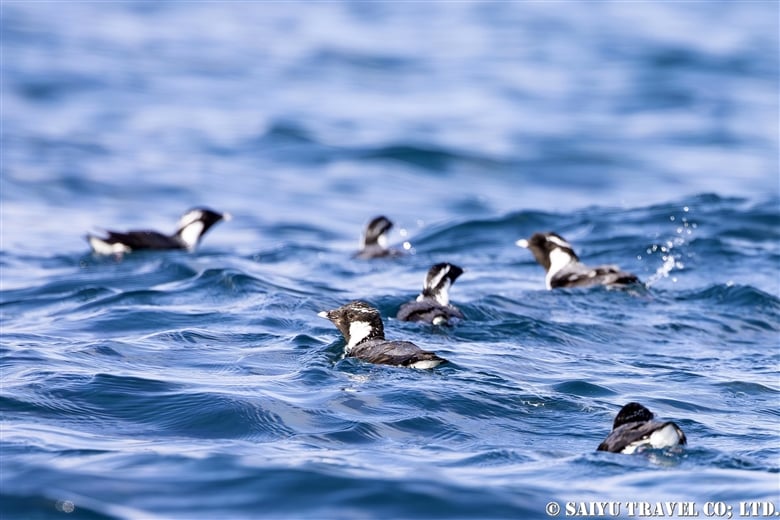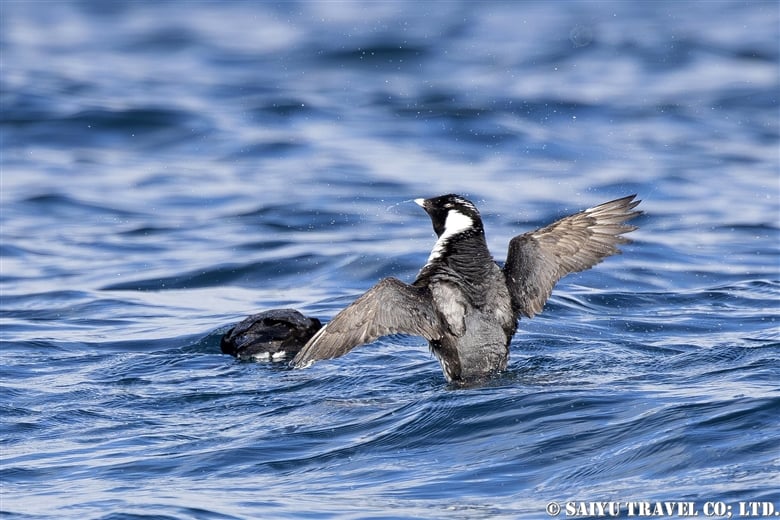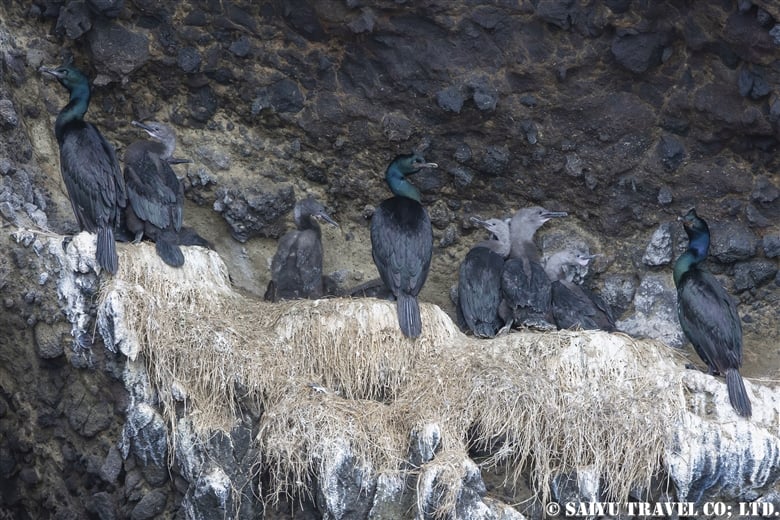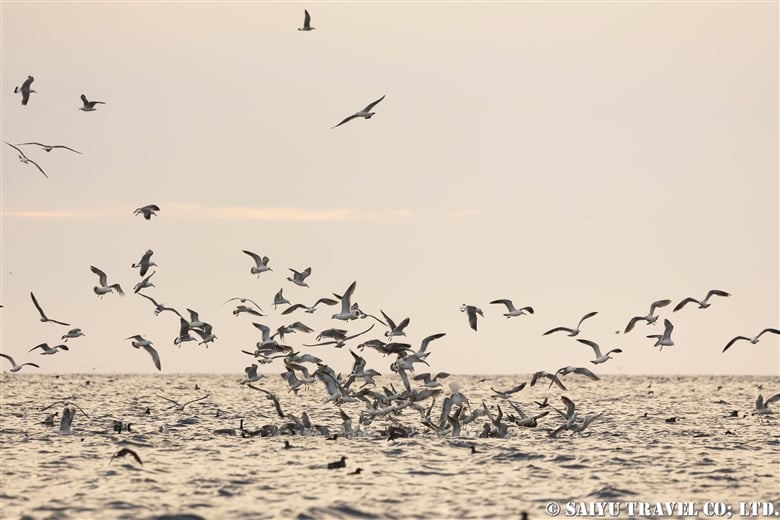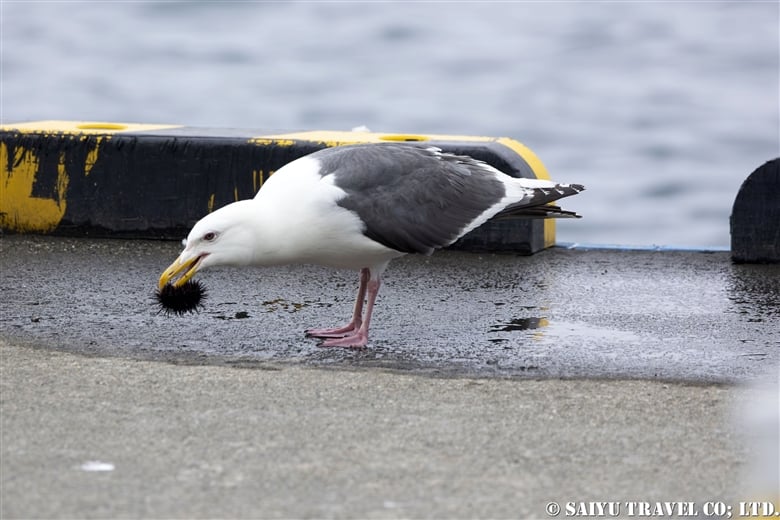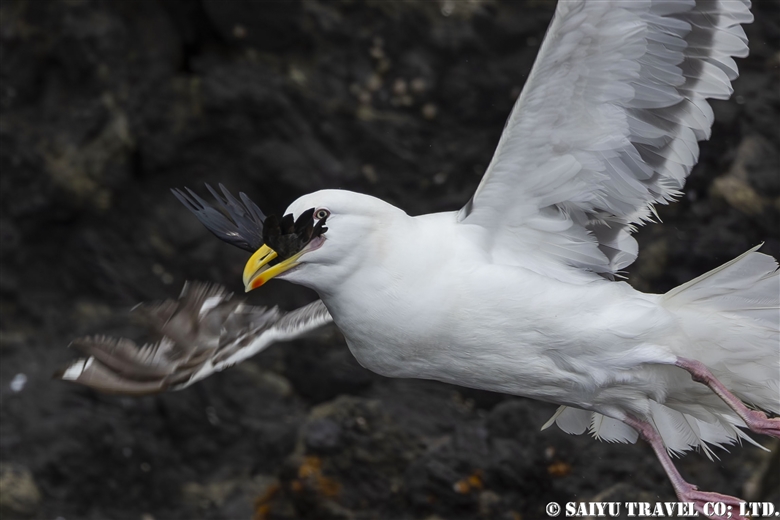
Teuri Island is a small island with a circumference of about 12 km, and as of 2024, it has a population of approximately 250 people. Despite its size, Teuri Island is considered a “paradise for seabirds,” with an estimated breeding population of around one million birds. Such a sanctuary for seabirds is unique within Japan, as even the neighboring Yagishiri Island, which is about 3 km to the east and of similar size, lacks a significant seabird population.
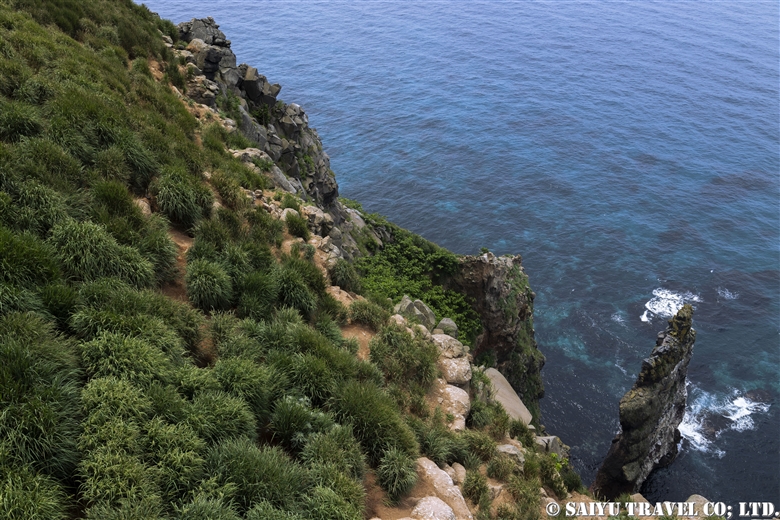
The reason behind this phenomenon can be attributed to the maritime climate around Teuri Island, particularly during winter when it is influenced by the Siberian high-pressure system from the continent. As a result, the island is continuously exposed to northwestern winds. Over millions of years, these prevailing winds have shaped the landscape, forming cliffs predominantly on one side of the island.
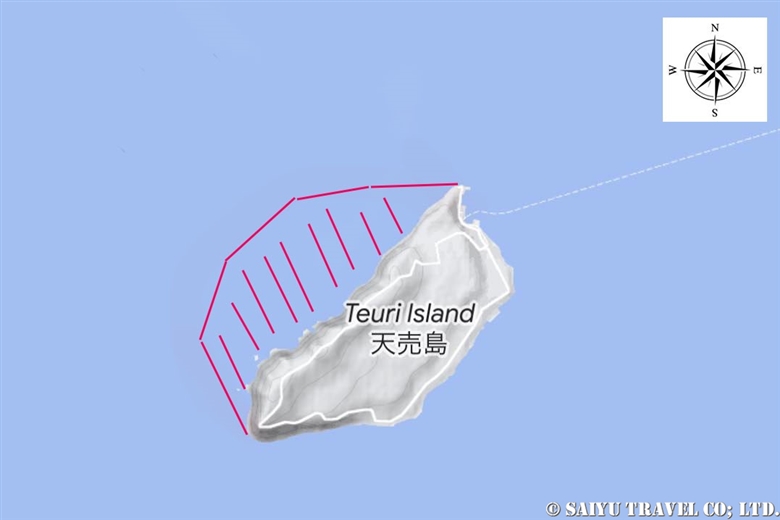
The red lines indicate the original location of the island.
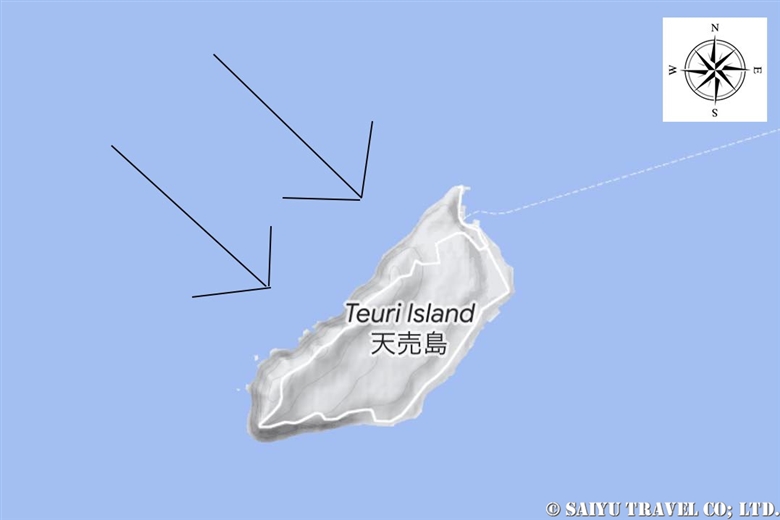
The arrows indicate the direction of the wind. Cliffs were formed on the northwest part of the island where the wind directly hits.
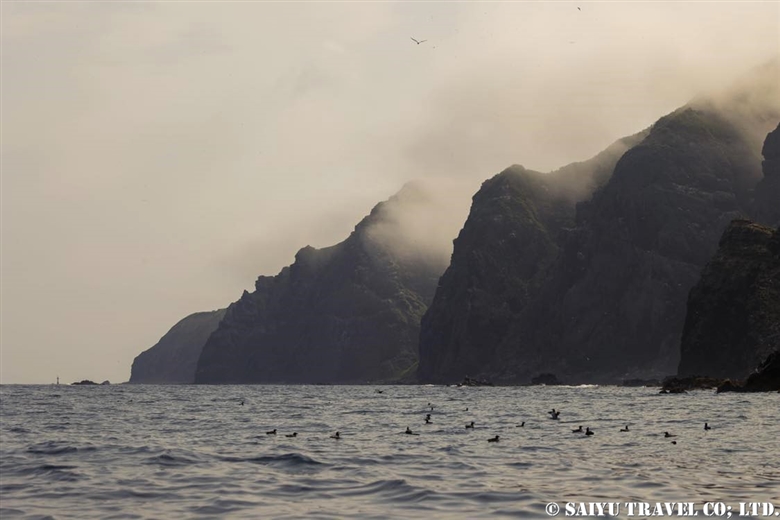

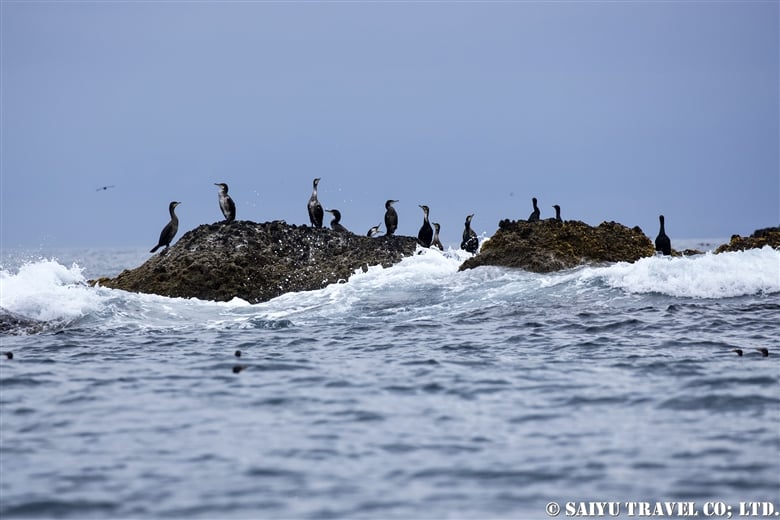
Cliffs, which are among the most challenging terrains for mammals, including humans, become easily accessible for birds capable of flying. Consequently, seabirds, which primarily reside at sea, are not well-adapted to terrestrial life, leading them to choose cliff habitats for breeding where their predators find it difficult to access.
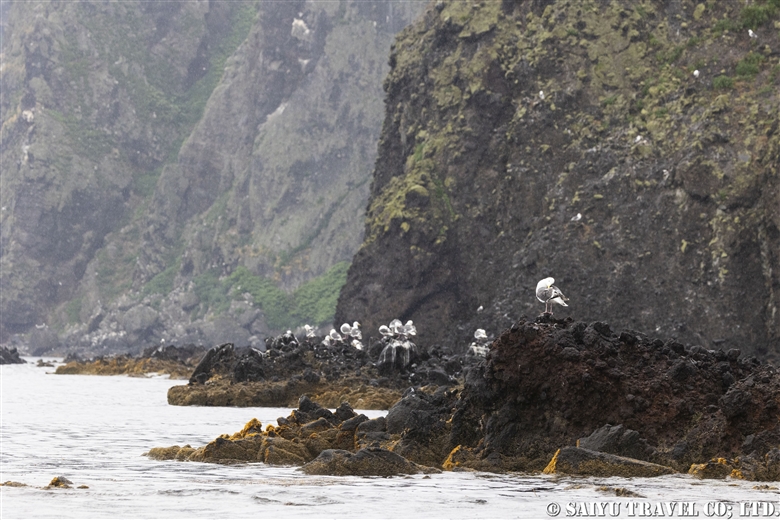

The slaty-backed gull, which breeds on cliffs.
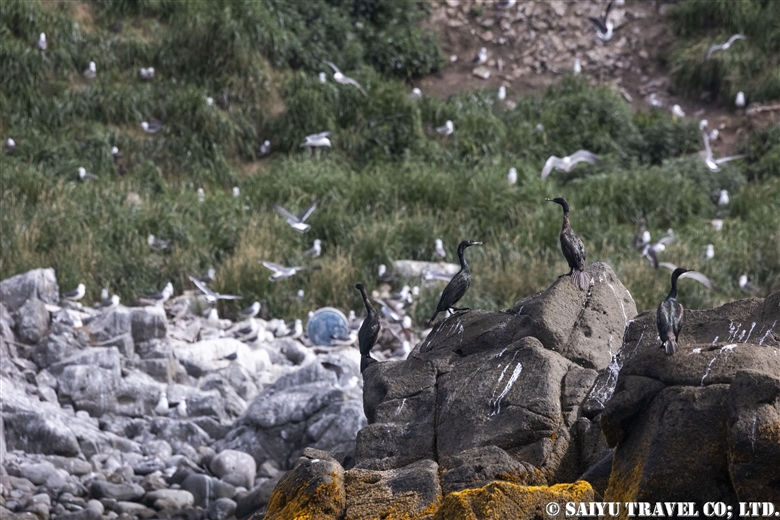

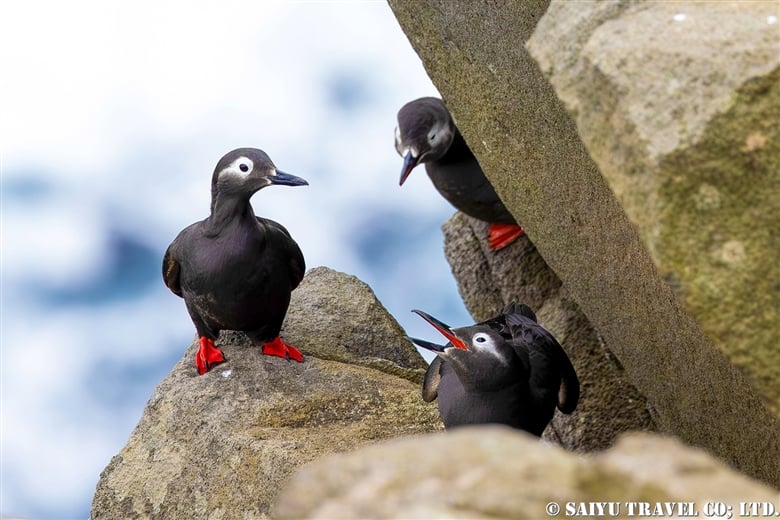
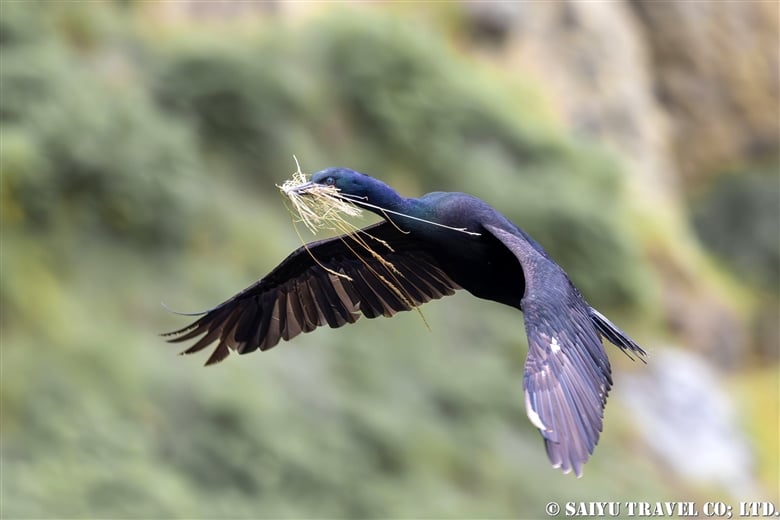
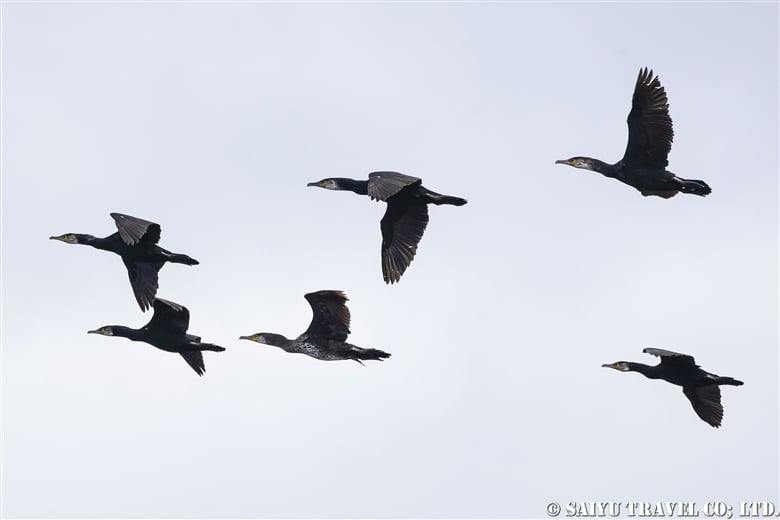
The pelagic cormorant and the black-tailed gull, which breed on cliffs.
The most abundant breeding location for rhinoceros auklets on Teuri Island is on land with soil situated atop the cliffs. Rhinoceros auklets choose to nest on land, despite the presence of many predators, as it becomes harder for predators to spot them during the evening twilight when they return to their nests all at once at sunset. If there were tall trees around the nesting area, they would be at a higher risk of colliding with them in the dark. Therefore, they prefer nesting in areas without tall trees.
Thanks to the island’s strong winds, which prevent the growth of tall trees, Teuri Island provides the ideal conditions for rhinoceros auklets. They have a habitat where approximately 400,000 breeding pairs thrive, making it the world’s No. 1 breeding site for these birds.
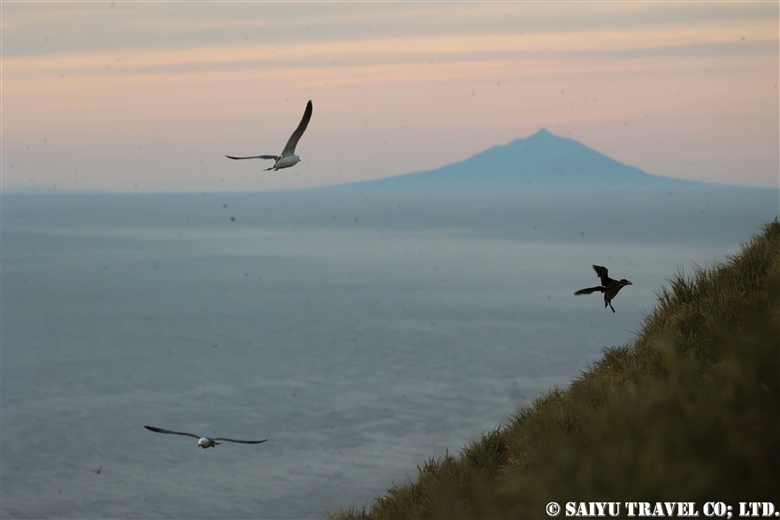

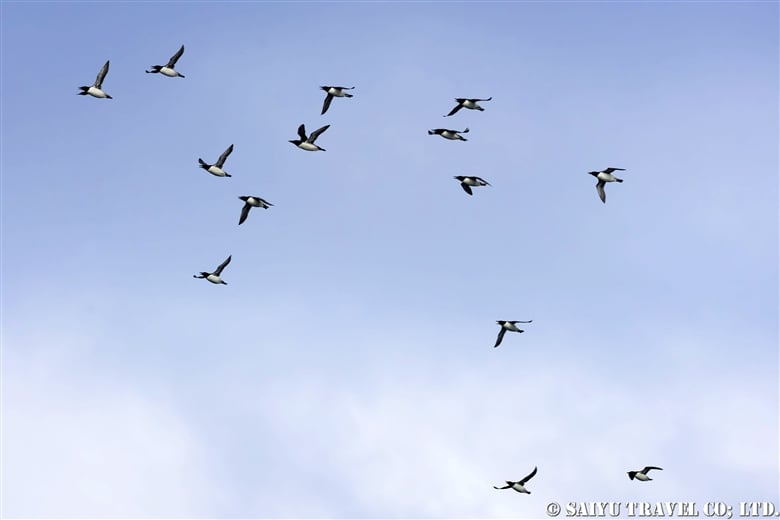
Rhinoceros auklets return to their nests by diving into treeless grasslands.
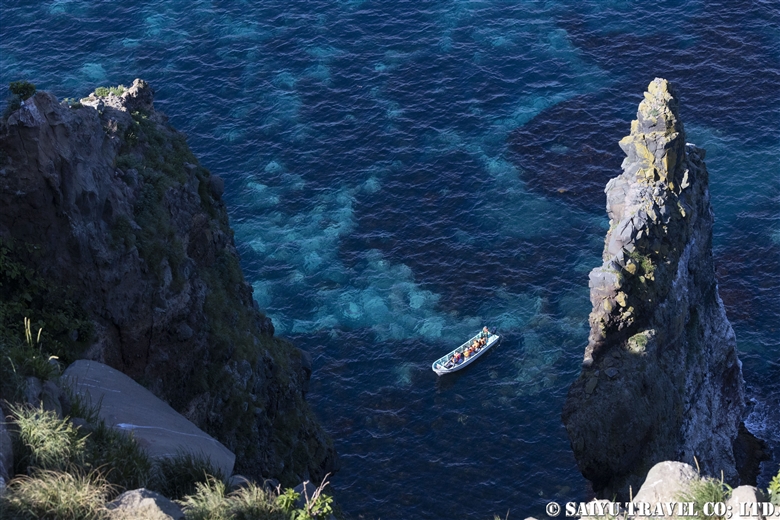

In this way, a miraculous convergence of ideal conditions for seabirds has resulted in the creation of Teuri Island, where numerous seabirds breed. During the seabird breeding season, boat tours are also available, allowing visitors to observe seabirds and geological formations from beneath the cliffs.
Photo & text : Wataru HIMENO
★ Visit our web site of TEURI ISLAND.
★Contact us to make arrangements for photographing seabirds on Teuri Island and Wildlife of Japan.
★Wildlife videos are also available on Youtube – we have the playlist as well.
Tags: Rhinoceros Auklet, Spectacled Guillemot, Teuri, 天売島, ケイマフリ, ウトウ, Wildlife tour in Japan, Bird photography in Japan, Wildlife tour of Japan, Pelagic Cormorant, Bird Photography Japan, Teuri Island, Bird Photography Hokkaido





















